What Is The Specific Name Of The Alpha Amylase Produced In Human And Animal Saliva?
Homo Salivary Amylase
Alexandra Simic Hachmann '17
Daniel Maffezzoli '17
Contents:
- I. Introduction
II. General Structure
3. Hydrolytic Activeness
IV. Bacterial Binding
V. References
I. Introduction
Human salivary alpha amylase (HSAmy) is an of import enzyme found in the oral cavity. It belongs to the glycoside hydrolase family and exists in diverse isoforms in salivary secretions. Humans produce two kinds of alpha amylase (salivary and pancreatic amylase) that overall share about 97% homology. HSAmy is a type of hydrolase that breaks down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars, similar glucose or maltose, by cleaving blastoff-ane,four-glucosidic bonds. Further breakdown of the starch is completed past pancreatic amylase after in digestion. This enzyme has distinct components including a calcium ion, chloride ion, and various amino acrid residues that play disquisitional roles in hydrolytic activity and substrate binding. HSAmy tin can besides bind to oral streptococci leaner. This results in the bacteria either being removed from or stored in the oral cavity. Storage and accumulation of the leaner in the oral cavity causes dental complications like plaque and molar decay. The structure of HSAmy consists of a single polypeptide chain of 496 amino acids that tin exist divided into iii domains. houses the agile site and contains three catalytic residues: Asp197, Glu233 , and Asp300. The neon structures are GLC sugars used for crystallography purposes and demonstrate the binding region. Hydrophobic ligands Arg337 , Arg195 and Asn298 function as binding sites for chloride ions, which are required for full catalytic activity. These bounden sites also contain hydrophobic residues ( Phe265 and Phe295) nearby that aid in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Just ane chloride ion and calcium ion bind per molecule of HSAmy. The is an important feature of homo salivary alpha amylase. The loop is glycine-rich, malleable, and holds the substrate in place during activity. It too plays a office in the release of product. The loop is in the "open" conformation when substrate is unbound, and is in the "off" position when a substrate is attached. The loop becomes more flexible and "opens" when information technology is fourth dimension for the products to be released. Then the bike restarts. When a carbohydrate binds to the active site (located in Domain A), the flexible loop becomes more than structured and as a event moves into contact with the substrate. His201 first detects the the substrate and causes the loop to take action. Later on the loop binds to the substrate, several residues play of import roles. Ala307 and Gly306 protect the substrate with a hydrophobic embrace, while residues Trp203 and Trp 284 (located on the secondary binding site) assist in hydrolytic activity. Trp59 and Tyr62 are involved in stacking to bind glucose and guide it to the catalytic residues. Effigy 1. Alpha-amylase catalyzing the hydrolysis of starch to glucose 2. Hsiu, Julia, Edmond H. Fischer, and Eric A. Stein. "Alpha-Amylases every bit Calcium-Metalloenzymes. 2. Calcium and the Catalytic Activity." Biochemistry including Biophysical Chemistry & Molecular Biology. ACS Publications, n.d. Web. 02 Dec. 2015. 3. Ramasubbu, Narayanan, Chandran Ragunath, Krishnan Sundar, Prasunkumar J. Mishra, Gy�ongyi Gy�m�nt, and Lili Kandra. "Structure-function Relationships in Human being Salivary blastoff-amylase: Role of Effluvious Residues." Academia. Academia, 2005. Web. 02 December. 2015. 4.Lebenthal, East. (1987). Role of salivary amylase in gastric and intestinal digestion of starch. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 32 (x), 1155-1157. 5. Butterworth, Peter J., Frederick J. Warren, and Peter R. Ellis. "Human Alpha-amylase and Starch Digestion: An Interesting Matrimony." Wiley Online Library, 5 January. 2011. Web. 02 December. 2015. 6. Nishide, T., Nakamura, Y., Emi, M., Yamamoto, T., Ogawa, G., Mori, T., Matsubara, K. (1986). Principal structure of human salivary blastoff amylase cistron. Factor, 41(2-3), 299-304. seven. "3BLK." RCSB PDB. PDB-101, Worldwide PDB Poly peptide Data Bank, EMDataBank, Ndb, Structural Biology Knowledgebase, n.d. Web. 02 Dec. 2015. 8. Ragunath, Chandran, Suba G.A. Manuel, Venkat Venkataraman, Hameetha B.R. Sait, Chinnasamy Kasinathan, and Narayanan Ramasubbu. "Probing the Role of Aromatic Residues at the Secondary Saccharide Bounden Sites of Man Salivary blastoff-amylase in Substrate Hydrolysis and Bacterial Bounden." Probing the Office of Aromatic Residues at the Secondary Saccharide Bounden Sites of Human Salivary blastoff-amylase in Substrate Hydrolysis and Bacterial Bounden 384.five (2008): 1232-248. Periodical of Molecular Biological science. U.South. National Library of Medicine, 14 Oct. 2008. Web. 02 Dec. 2015.
Model View:
II. Full general Construction
consists of one calcium binding site. HSAmy is a calcium metalloenzyme and therefore cannot role efficiently in the absence of calcium. The ion serves as a stabilizer during hydrolytic activity and is held in identify by residues Arg158, Asn100, Asp167, and His201. is bundled in a Beta-construction and its office is still unknown. III. Hydrolytic Activity
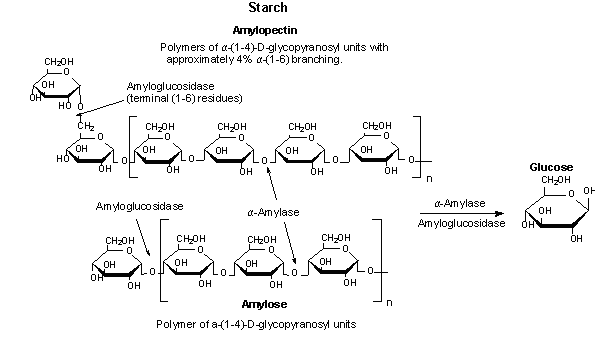
IV. Bacterial Binding
Between fluctuations in pH, temperature, nutrient supply, and saliva flow, the oral cavity is a challenging location for bacteria to persist. Human salivary alpha-amylase binds to oral streptococci in a like fashion as information technology does to complex carbohydrates. When breaking down bacteria, His201 and His305 are necessary to observe bacterial and starch substrates, while the flexible loop attaches and changes conformation, holding the substrate in place. Trp58 is vital for optimal hydrolytic activity. It detects substrates and is thought to help in the orientation of the substrate, likewise as assist His305 to its correct position.
Five. References
Source: https://biology.kenyon.edu/BMB/jsmol2015/3BLKAmylase/index4.html
Posted by: fullertonsulthen.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Specific Name Of The Alpha Amylase Produced In Human And Animal Saliva?"
Post a Comment